
Large Loss of Alaska Permafrost Projected by 2100
December 02, 2015
Wednesday AM
(SitNews) - Northern latitude tundra and boreal forests are experiencing an accelerated warming trend that is greater than in other parts of the world according to the United Stated Geological Society. This warming trend degrades permafrost, defined as ground that stays below freezing for at least two consecutive years. Some of the adverse impacts of melting permafrost are changing pathways of ground and surface water, interruptions of regional transportation, and the release to the atmosphere of previously stored carbon.
Using statistically modeled maps drawn from satellite data and other sources, U.S. Geological Survey scientists have projected that the near-surface permafrost that presently underlies 38 percent of boreal and arctic Alaska would be reduced by 16 to 24 percent by the end of the 21st century under widely accepted climate scenarios. Permafrost declines are more likely in central Alaska than northern Alaska.
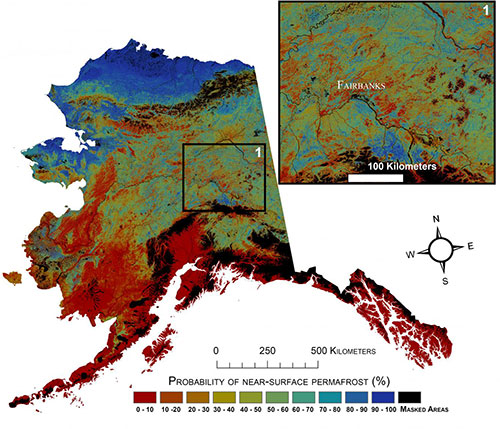
Current probability of near-surface permafrost in Alaska
Click here or on map for a larger view...
Courtesy USGS
"A warming climate is affecting the Arctic in the most complex ways," said Virginia Burkett, USGS Associate Director for Climate and Land Use Change. "Understanding the current distribution of permafrost and estimating where it is likely to disappear are key factors in predicting the future responses of northern ecosystems to climate change."
In addition to developing maps of near-surface permafrost distributions, the researchers developed maps of maximum thaw depth, or active-layer depth, and provided uncertainty estimates. Future permafrost distribution probabilities, based on future climate scenarios produced by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), were also estimated by the USGS scientists. Widely used IPCC climate scenarios anticipate varied levels of climate mitigation action by the global community.
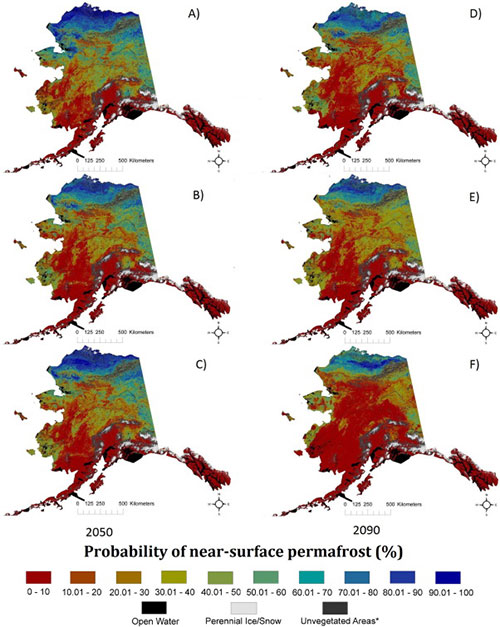
Future permafrost distribution probabilities, based on future climate scenarios produced by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
Click here or on the map for a larger view...
Courtesy USGS
These future projections of permafrost distribution, however, did not include other possible future disturbances in the future, such as wildland fires. In general, the results support concerns about permafrost carbon becoming available to decomposition and greenhouse gas emission.
The research has been published in Remote Sensing of Environment. The current near-surface permafrost map is available via ScienceBase.
Edited by Mary Kauffman, SitNews
Source of News:
USGS
www.usgs.gov
Publish A Letter in SitNews
Contact the Editor
SitNews ©2015
Stories In The News
Ketchikan, Alaska
|
Articles &
photographs that appear in SitNews may be protected by copyright
and may not be reprinted without written permission from and
payment of any required fees to the proper sources.
E-mail your news &
photos to editor@sitnews.us
Photographers choosing to submit photographs for publication to SitNews are in doing so granting their permission for publication and for archiving. SitNews does not sell photographs. All requests for purchasing a photograph will be emailed to the photographer.
|
|


